Surgery Made Safer: Reduce Complications by 32% and Save $3,720 Per Operation
The only medical 3D printing service that guarantees surgical precision
– trusted by leading surgeons to save lives and reduce costs
When Dr. Stefan Arsenkov needed to remove a tumor embedded deep within his patient’s liver, he knew the margins were razor-thin – one miscalculation could damage vital blood vessels or leave cancerous tissue behind. Using our patient-specific 3D model, he mapped every vessel and tumor boundary beforehand, completing the complex resection in record time with millimeter precision. His patient’s liver function remained perfect, and they were discharged two days ahead of schedule.
Your surgical outcomes are too important to leave to chance
The Problem Every Surgeon Faces
Complex anatomies. Unexpected complications. Longer operation times. Higher costs. Lower confidence.
Traditional 2D imaging leaves you guessing about critical anatomical variations that only become apparent when it’s too late to adjust your approach.
The 3DLoom Solution: Surgical Certainty
Our 3D printing technology transforms your DICOM files into anatomically perfect replicas that you can hold, study, and practice on before making the first incision.
Proven Results from 50+ Surgeries:
Better Outcomes
32% fewer complications in complex cases
Reduced Surgical Time
30-40 minutes average time reduction per surgery
Increased Precision
47% improvement in surgical accuracy
Enhanced Confidence
94% of surgeons report increased confidence with 3D printed models.
Services Designed for Surgical Excellence
Custom solutions tailored to your specific surgical and educational needs
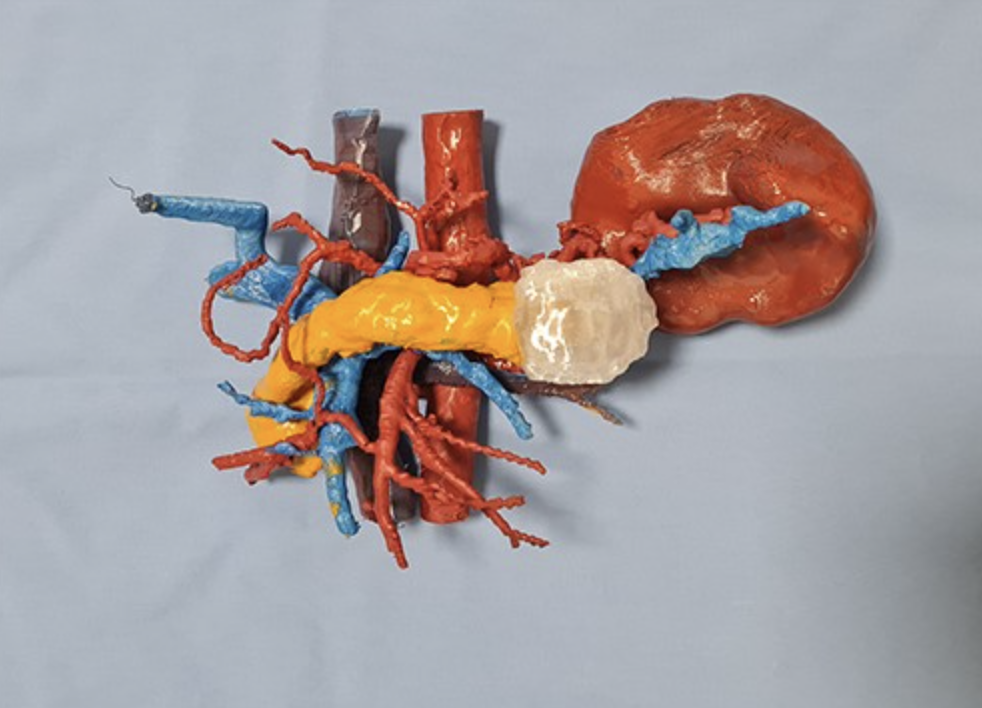
Patient-Specific Anatomical Models
Hold your patient’s exact anatomy in your hands before surgery Perfect for tumor resections, complex reconstructions, and high-risk procedures.

Custom Surgical Guides
Precision instruments that eliminate guesswork Designed specifically for your patient’s unique anatomy and your preferred approach.
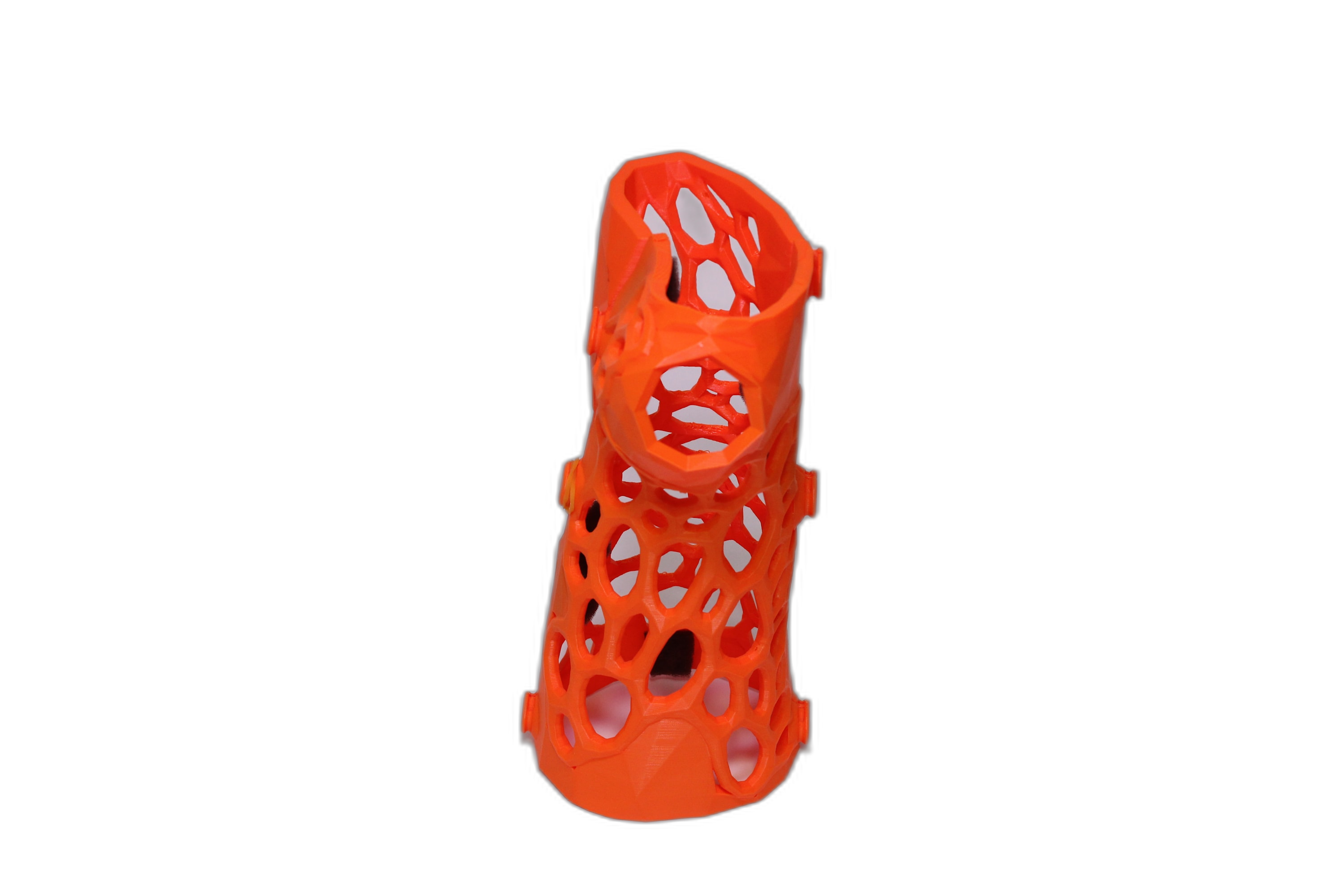

Educational Models
Train your team and educate patients with confidence Improve surgical training outcomes and patient understanding.
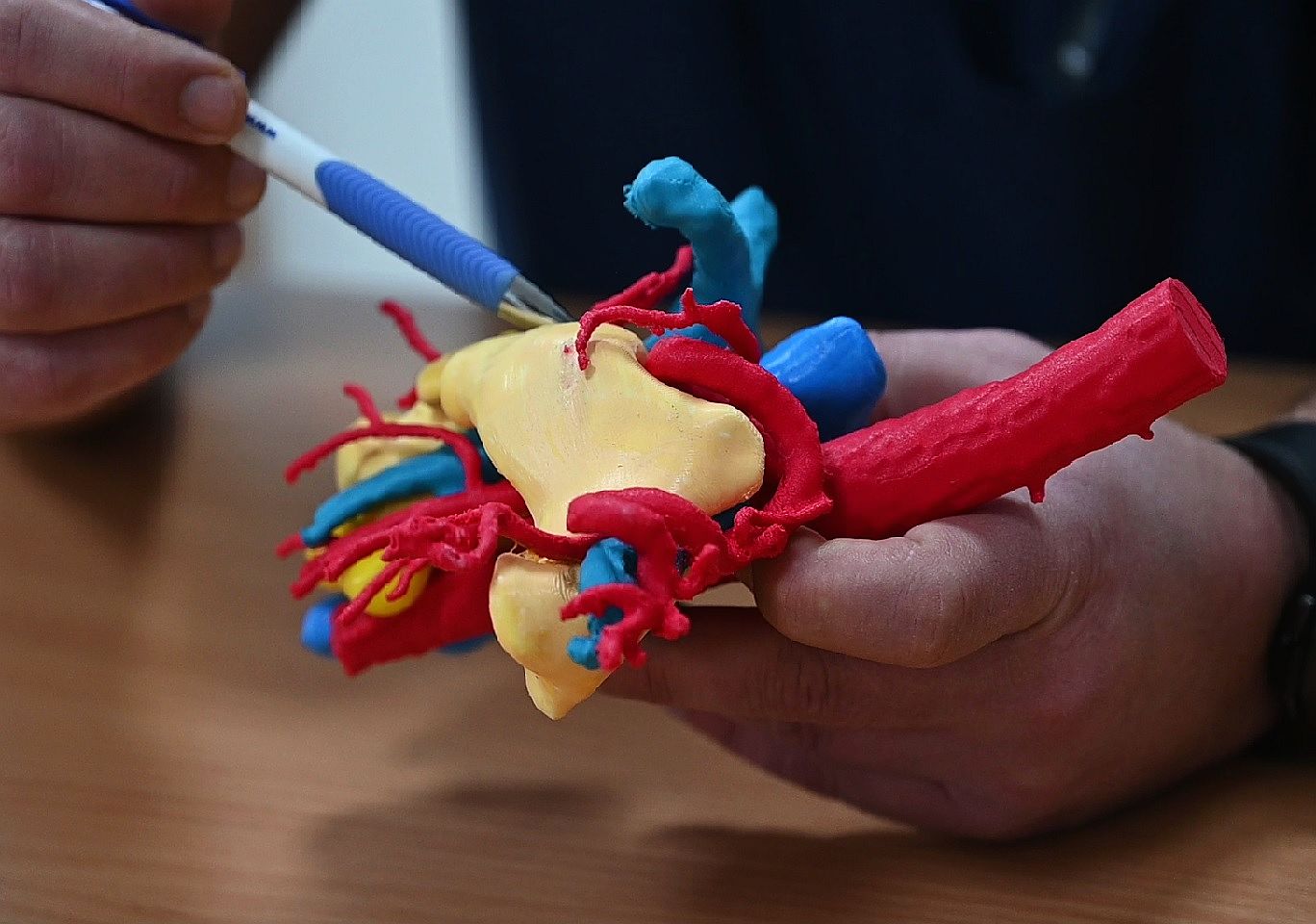
Educational Organ Models
Detailed anatomical models for medical training and patient education.
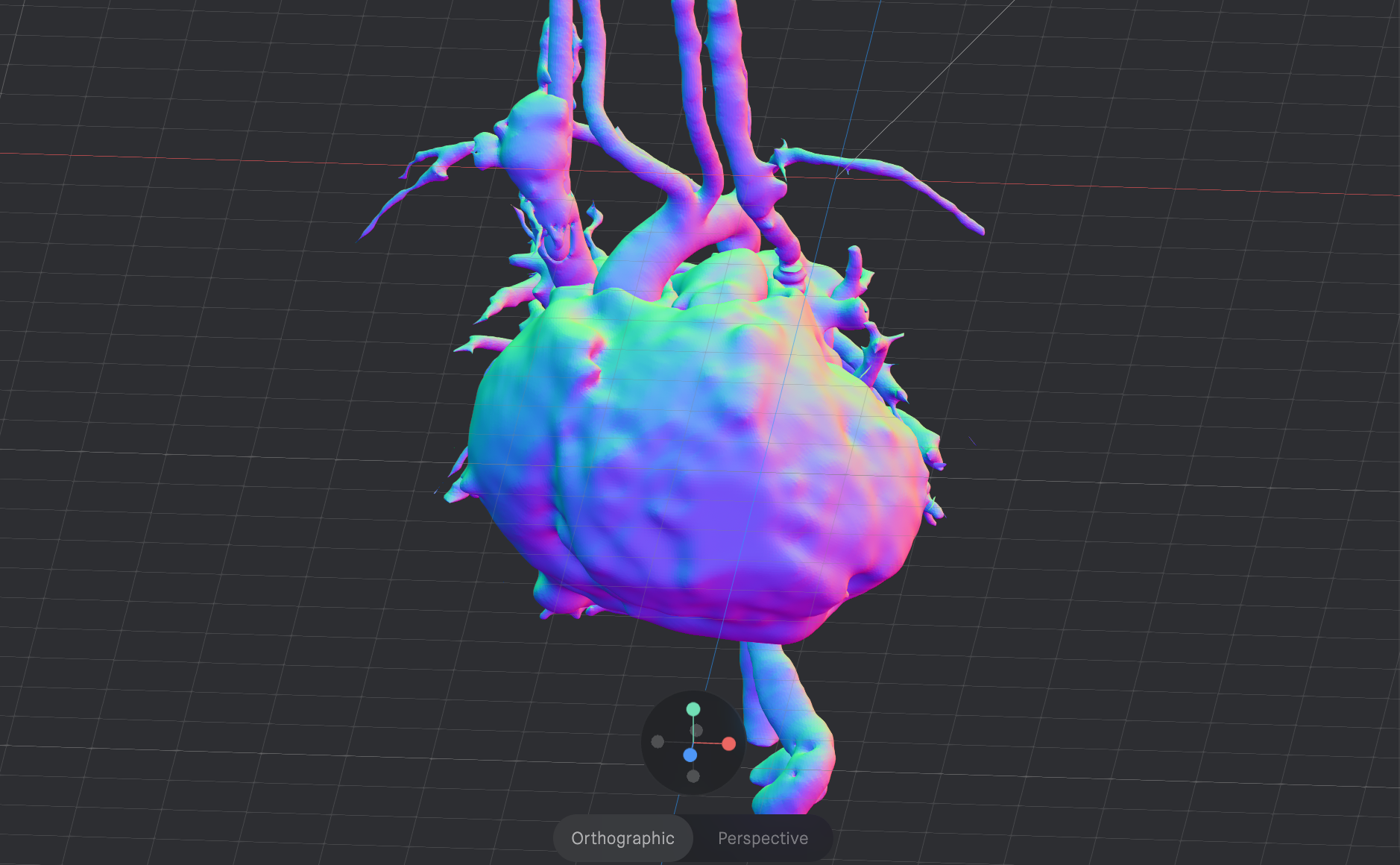
VR/AR Models
Interactive virtual and augmented reality models for immersive planning.

Consulting Services
Expert guidance on implementing 3D printing in your medical practice.
Addressing Your Concerns
"Will this disrupt our workflow?"
Our streamlined 5-step process integrates seamlessly with your existing protocols. Most hospitals are operational within 2 weeks.
"How quickly can we see ROI?"
Break-even typically occurs after just 63 cases. Medium-sized hospitals save $185,000-$370,000 annually.
"Do we need special training?"
Our team provides comprehensive training and ongoing support. Most surgical teams are proficient within one week.
Measurable Impact & ROI
Our technology delivers significant clinical and financial benefits
Per Surgery Impact
-
$3,720 saved per surgery on average
Reduced OR time and fewer complications
-
62 minutes reduction in average OR time
More efficient surgical planning
-
32% fewer complications in complex cases
Improved patient outcomes
-
Up to $13,000 avoided in complication costs
Reduced readmissions and follow-up care
Hospital-Wide Savings
- Break-even with just 63 cases per year
Rapid return on investment - $185,000–$370,000 annual savings
For medium-sized hospitals - $130,000+ yearly orthopedic department savings
Specialty-specific benefits - 1.2 days reduced average hospital stay
Improved patient throughput
Healthcare System Impact
- $7–$15 billion potential yearly national savings
If adopted widely - $50+ billion addressable market
Growing adoption of medical 3D printing - Significant reduction in surgical waste
More sustainable healthcare - Enhanced surgical training
Better prepared medical professionals
Impactful 3D Printing Statistics
- Reduction in Surgical Time 41%
- Fewer complications 32%
- Reduced average hospital stay 23%
%
Accuracy in implant placement or tumor resection margins
Trusted by Leading Surgeons
Hear from medical professionals who have transformed their practice with our 3D printing solutions

★★★★★
My experience with using 3DLoom’s 3D printed models is exceedingly positive. For the cases I used the models, not only did my understanding of the patient’s specific anatomy was better, I was able to finish the operation in a much shorter time than usual, saving on average 30-40 minutes of operative time.
Dr. Labinot, Bekteshi – Traumatologist

★★★★★
I have used the 3D printed models for preoperative planning and my impression was that my confidence during the surgery itself was much higher, because I was fully aware of the anatomical variations present in the patient. This enabled me to work not only with greater efficiency but with a higher degree of safety for the patient.
Dr. Valon Saliu – Abdominal surgeon

★★★★★
3D models have been invaluable tools in surgical planning, offering unmatched insight into patient anatomy. They give me a thorough understanding of complex structures, allowing for detailed preoperative planning and accurate intraoperative navigation. Physically interacting with them enhances confidence and leads to improved surgical outcomes.
Dr. Risto Pejkov – Urologist/Urologic Surgeon
Our Simple 5-Step Process
From medical imaging to surgical planning – seamless and efficient

Submit Your Medical Imaging
Send us your DICOM files (CT, MRI, X-ray)

Consultation & Custom Design
Our experts create your 3D model

Precision 3D Printing
High-quality medical-grade printing

Quality Verification
Rigorous accuracy checks

Delivery & Support
Fast shipping and planning support
Take the Next Step with 3DLoom
Unlock the full potential of your surgical planning with our cutting-edge 3D printing solutions. Experience reduced operation times, fewer complications, and significant cost savings. Schedule a consultation today to see how 3DLoom can transform your practice.
